Tax implications of solar panels
Welcome to our dedicated page for Tax implications of solar panels! Here, we have carefully selected a range of videos and relevant information about Tax implications of solar panels, tailored to meet your interests and needs. Our services include high-quality Tax implications of solar panels-related products and solutions, designed to serve a global audience across diverse regions.
We proudly serve a global community of customers, with a strong presence in over 20 countries worldwide—including but not limited to the United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, the United Kingdom, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, the Netherlands, Australia, India, Japan, South Korea, China, Russia, South Africa, Egypt, Turkey, and Saudi Arabia.
Wherever you are, we're here to provide you with reliable content and services related to Tax implications of solar panels. Explore and discover what we have to offer!

Incentives for solar power generation systems
Personal-use solar power systems are eligible for a federal income tax credit under Sec. 25D. This credit is available only for the taxpayer''s personal residence and equals up to 30% of the costs of qualified property
Read more
Solar Panel Installation Cost | Understanding Solar
The relationship between the presence of solar panels and changes in property tax rates is a topic of interest for residents seeking to understand the potential financial implications of renewable energy investments. Solar panel installation
Read more
Final section 6C solar incentive guide for individuals
This 17-page guide provides general guidance on the newly introduced solar energy tax credit (for natural persons) under section 6C of the Income Tax Act 58 of 1962, and contains 3 practical examples (where the facts
Read more
Residential Clean Energy Credit
Understanding the tax ramifications of solar panels is critical for optimizing your savings while also helping to a more environmentally friendly future. In this post, we''ll look at federal, state, and local tax breaks, company
Read more
What is the solar tax incentive for businesses in South
1. Normal Tax As of 1 March 2023, South African businesses can qualify for a 125% tax deduction on qualifying investment costs for renewable energy projects, with no thresholds on generation capacity. This is intended to be a temporary
Read more
Solar tax deductions for businesses: expansion of existing incentive
Solar tax deductions for businesses: expansion of existing incentive 20 March 2023 Accounting South African Accounting Academy As stated in the 2023 Budget Speech, the tax incentive
Read more
Understanding Solar Renewable Energy Credits Taxable Income
2 天之前· The financial benefits derived from generating solar power, often in the form of tradable instruments, can have implications for tax obligations. These instruments, representing the
Read more
Maximizing Tax Benefits with Solar Power Systems
As energy costs rise and sustainability becomes a global priority, solar power systems are gaining traction as a smart and eco-friendly investment. Beyond reducing electricity bills and promoting green living, solar
Read more
A Comprehensive Guide to South Africa''s Solar Tax
A solar tax incentive is a form of financial support offered by the government to encourage investment in solar energy. This can take the form of tax credits, rebates, deductions, or exemptions. In South Africa, two primary
Read more
Homeowner''s Guide to the Federal Tax Credit for Solar
What is a tax credit? A tax credit is a dollar-for-dollar reduction in the amount of income tax you would otherwise owe. For example, claiming a $1,000 federal tax credit reduces your federal
Read more
Are Solar Energy Credits Taxable?
Understanding the tax implications of solar energy credits is vital, especially when it comes to income reporting requirements. As residential solar users, we need to know how to report any financial benefits we receive.
Read more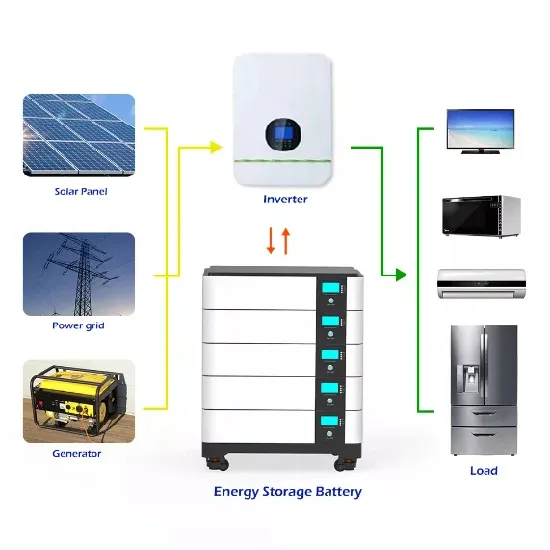
Solar Energy Development Opportunities: Tax Implications
Solar Energy Development Opportunities: Tax Implications For some landowners, renting their land for use as solar farms has emerged as an intriguing alternative to renting for agricultural or
Read moreFAQs 6
How does the solar tax credit affect residential solar?
Here’s is how this law impacts residential solar: The 30% solar tax credit claimed by homeowners (25D) would be terminated at midnight on December 31, 2025. Homeowners who have their systems installed before the end of the year can still claim this credit against their federal tax liability.
Are solar facilities taxable?
In addition to tax credits or grant payments, solar facilities also can generate significant tax losses that can be valuable to owners with other sources of taxable income that can be offset by the losses. MACRS Depreciation.
What are the tax benefits of solar power?
The tax benefits can include income tax credits, breaks on local real estate taxes, and enhanced depreciation of solar assets. However, the advantages extend beyond income tax incentives, as many states, power companies, and municipalities offer additional incentives, such as partial reimbursements or purchases of excess power generation.
Do solar panels qualify for a federal tax credit?
The answer depends heavily on your specific circumstances. The IRS states in Questions 25 and 26 in its Q&A on Tax Credits18 that off-site solar panels or solar panels that are not directly on the taxpayer’s home could still qualify for the residential federal solar tax credit under some circumstances.
Are solar panels tax deductible?
Under most circumstances, subsidies provided by your utility to you to install a solar PV system are excluded from income taxes through an exemption in federal law.11 When this is the case, the utility rebate for installing solar is subtracted from your system costs before you calculate your tax credit.
How does depreciation affect solar energy investments?
As solar energy gains traction among businesses and homeowners, understanding the financial aspects of solar panel investments is essential. Depreciation plays a significant role in determining the cost-effectiveness of such investments, influencing both accounting practices and tax liabilities.

